The ATP molecules is an immediate source of energy that drives the functions of cell. Which type of organic molecule is most commonly used as energy for cells.

The Molecule That Serve As The Immediate Energy Source For Most Chemical Reactions Within The Cell Is A Atp B Adp C Amp D Sucrose Study Com
The molecule that provides energy for every cell is glucose.
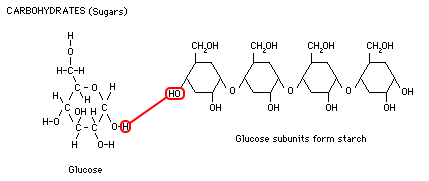
. A simple monosaccharide sugar with a molecular formula of C6H12O6. -transfers energy to cell processes ADP adenosine diphosphate a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate group ATP and ADP The break down of ATP to ADP and the production of ATP from ADP is a cycle. Adenosine Triphosphate ATP A molecule that provides energy for cellular reactions and processes.
Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. -not a simple process -large complex group of proteins is needed. What is the energy storage molecule in plants.
It is a principal source of energy for cellular metabolism Metabolism of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are one of the major forms of energy for animals and plants. Instructions for building proteins DNA provides immediate energy glucose sex hormones steroid provides short-term energy storage for plants sucrose starch carbohydrates forms the cell membrane of all cells phospholipids speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy enzyme one sugar monosaccharide cells convert this to ATP glucose. Living things consume sugar as a major energy source because sugar molecules have a great deal of energy stored within their bonds.
The storage form of glucose in plants is starch. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. An ATP molecule has a head of adenose sugar and a tail of three phosphate groups.
This is a classic example of one of the many cellular processes that use and produce energy. During the chemical reactions of photosynthesis energy is provided in the form of a very high-energy molecule called ATP or adenosine triphosphate which is the primary energy currency of all cells. What is the functions of lipids.
Ultimately the end product is. This process is a fundamental and efficient way for. Starch is a polysaccharide.
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. It is produced from respiration in the mitochondria. Most of the respiration process occurs in the mitochondria of the cell but the initial stage starts in the cytoplasm and cytosol.
The leaves of a plant make sugar during the process of photosynthesis. ATP structure A nucleotide made of an adenine base a ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. It is broken down during cellular respiration into carbon dioxide water.
For each molecule of glucose two molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to provide energy to drive the early steps but four molecules of ATP are produced in the later steps. For the most part photosynthesizing organisms like plants produce these sugars. The unit of Cellular Energy ATP is the most important storage molecule that provides chemical energy to the cell for a variety of cellular reactions.
Living things consume sugars as a major energy source because sugar molecules have a great deal of energy stored within their bonds. ATP releases energy when one of its high-energy bonds is broken to release a phosphate group. Energy the ability to do work Metabolism all of the chemical reactions in a cell Photosynthesis.
The process that builds molecules by removing water to bind them together is answer choices Hydrolysis Protein Synthesis Dehydration Synthesis Lysis Question 10 20 seconds Q. Consider the metabolism of sugar. Organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes.
ATP is the molecule that provides energy for cells in daily processes. ATP is the most important biological molecule that provides chemical energy Cellular Respiration is the catabolic pathway in which organic molecules are broken down to release energy for use by a cell. The metabolism of sugar a simple carbohydrate is a classic example of the many cellular processes that use and produce energy.
Also called a consumer. Which type of organic molecule is most commonly used as energy for cells. The breakdown of glucose a simple sugar is described by the equation.
The amount of energy needed to make one glucose molecule from six carbon dioxide molecules is 18 ATP molecules and 12 NADPH molecules each one of which is energetically equivalent to three ATP molecules or a total of 54 molecule equivalents required for synthesizing one glucose molecule. Answer choices Quick source of energy Builds muscles skin enzymes Stores genetic information Stores energy insulation protection. Thus most of the fundamental concepts discussed in this chapter have been.
And it was quickly followed by the recognition of the central role of ATP in cellular processes. ATP can transfer energy and phosphorylate add a phosphate to other molecules in cellular processes such as DNA replication active transport synthetic pathways and. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate consisting of a nitrogenous base adenine a ribose sugar and three serially bonded phosphate groups.
The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate consisting of a nitrogenous base adenine a ribose sugar and three serially bonded phosphate groups. Just as the dollar is used as currency to buy goods cells use molecules of ATP as energy currency to perform immediate work.

Three Energy Systems In The Body What Is An Immediate Energy System Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Adenosine Triphosphate Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica
0 Comments